
1 自适应光学全国重点实验室,四川 成都 610209
2 中国科学院光电技术研究所,四川 成都 610209
3 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
4 山东高等技术研究院,山东 济南 250100
Overview: Gravitational waves are spacetime oscillations radiated outward by accelerating mass objects. Significant astronomical events in the universe, such as the merging of massive black holes, emit stronger gravitational waves. Detecting gravitational waves allows for a deeper study of the laws governing celestial bodies and the origins of the universe, making accurate detection crucial. Gravitational wave detection technology utilizes Michelson interferometers to convert the extremely faint spacetime fluctuations caused by gravitational waves into measurable changes in optical path length. Recently, ground-based large Michelson interferometers have achieved direct detection of high-frequency gravitational waves. However, the detection of low-frequency gravitational waves, which is equally important, is not feasible on the ground due to arm length and ground noise issues. This necessitates the construction of ultra-large Michelson interferometers in space for low-frequency gravitational wave detection. Spaceborne gravitational wave detection telescopes play a vital role in collimating bidirectional beams in ultra-long interferometric optical paths in space. The extremely subtle changes in optical path caused by gravitational waves impose high demands for pm-level optical path length stability and below 10?10 level backscattered light in these telescopes. The ultra-high level index requirements exceed the precision limits of current ground testing techniques for telescopes. To ensure that spaceborne telescopes maintain their ultra-high design performance in the orbital environment, developing testing and evaluation techniques for these key indicators is a crucial prerequisite for the success of the space gravitational wave detection program. This paper provides an overview of the development of spaceborne gravitational wave detection telescopes, both domestically and internationally. It focuses on the current status and some test results of optical path length stability and backscattered light testing of telescopes under development, as well as further testing plans, providing a reference for the testing and evaluation of Chinese space gravitational wave detection space-borne telescopes.
空间引力波探测 星载望远镜 地面测试 光程稳定性 后向杂散光 space gravitational wave detection spaceborne telescope ground test optical path length stability backscattered light 红外与激光工程
2023, 52(7): 20220887
1 中国科学院自适应光学重点实验室,四川 成都 610209
2 中国科学院光电技术研究所,四川 成都 610209
3 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
在天文大视场高分辨率成像领域,对地表层自适应光学(Ground-Layer Adaptive Optics, GLAO)系统作出准确的理论评估是系统设计与优化的关键前提。在GLAO技术中,地表层湍流特性与导引星布局是影响系统性能的重要因素。针对不同湍流环境与导引星位置分布,基于空间频谱滤波理论和蒙特卡洛方法对GLAO系统进行理论分析与性能评价工作,从而验证两种方法的正确性与准确性。结果表明,两种模型得到的系统校正规律呈现明显的一致性。在一定条件下,两种方法数值模拟偏差最大不超过4.6%。空间频谱滤波原理将系统简化为线性模型,其计算速度更快,便于发现系统特征规律,但是该方法适用于导引星呈对称布局的系统性能分析,不适用于非对称排布的任意导星布局解析分析。蒙特卡洛方法结合真实系统的物理过程进行实时模拟,其导引星布局可以任意设置,对于系统实际运行状态的预测更加准确。在两种分析方法对比的基础上,进一步针对系统布局给出了初步的优化结果,相关工作对未来GLAO系统的设计与优化具有指导意义。
地表层自适应光学 空间频谱滤波理论 蒙特卡洛 导引星 ground-layer adaptive optics spatial frequency spectrum filtering theory Monte Carlo guide stars 红外与激光工程
2022, 51(7): 20210744
1 中国科学院自适应光学重点实验室,四川 成都 610209
2 中国科学院光电技术研究所,四川 成都 610209
3 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
对太阳大气进行大视场高分辨力光学成像观测是开展太阳物理、空间天气等基础与应用研究的重要前提。对于地基太阳望远镜而言,为了消除地球大气湍流对光学系统的影响,自适应光学是高分辨力成像观测必备的技术手段,与此同时,为了突破大气非等晕性对传统自适应光学校正视场的限制,近年来多层共轭自适应光学技术等大视场自适应光学得到极大发展。本文首先梳理国外太阳自适应光学系统研制情况,重点介绍国内太阳自适应光学技术发展及应用情况,并进一步介绍了后续大视场太阳自适应光学技术发展情况以及目前所取得的成果。
太阳观测 自适应光学 多层共轭自适应光学 solar observation adaptive optics multi-conjugate adaptive optics
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 The Key Laboratory on Adaptive Optics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
2 The Laboratory on Adaptive Optics, Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
3 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
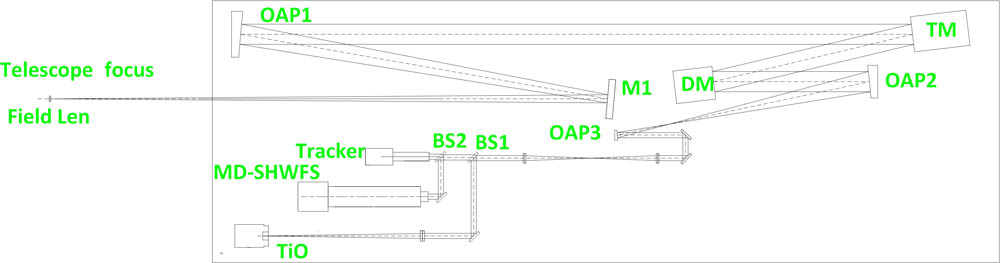
A prototype of a solar ground-layer adaptive optics (GLAO) system, which consists of a multi-direction correlating Shack–Hartmann wavefront sensor with 30 effective subapertures and about a 1 arcmin field of view (FoV) in each subaperture, a deformable mirror with 151 actuators conjugated to the telescope entrance pupil, and a custom-built real-time controller based on field-programmable gate array and multi-core digital signal processor (DSP), is implemented at the 1 m New Vacuum Solar Telescope at Fuxian Solar Observatory and saw its first light on January 12th, 2016. The on-sky observational results show that the solar image is apparently improved in the whole FoV over 1 arcmin with the GLAO correction.
010.1080 Active or adoptive optics 110.1080 Active or adoptive optics Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(10): 100102

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 The Key Laboratory on Adaptive Optics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
2 The Laboratory on Adaptive Optics, Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
3 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
A second generation solar adaptive optics (AO) system is built and installed at the 1-m New Vacuum Solar Telescope (NVST) of the Fuxian Solar Observatory (FSO) in 2015. The AO high-order correction system consists of a 151-element deformable mirror (DM), a correlating Shack–Hartmann (SH) wavefront sensor (WFS) with a 3500 Hz frame rate, and a real-time controller. The system saw first light on Mar. 16, 2015. The simultaneous high-resolution photosphere and chromosphere images with AO are obtained. The on-sky observational results show that the contrast and resolution of the images are apparently improved after the wavefront correction by AO.
010.1080 Active or adoptive optics 110.1080 Active or adoptive optics 110.0115 Imaging through turbulent media Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(12): 120101





